The global off-grid hybrid power systems market has taken center stage. As countries strive to meet carbon reduction goals and promote energy independence, off-grid hybrid power systems have gained significant attention. These systems, which combine renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydro with traditional energy generation methods, are revolutionizing how electricity is provided to remote and underserved communities.
Understanding Off-Grid Hybrid Power Systems
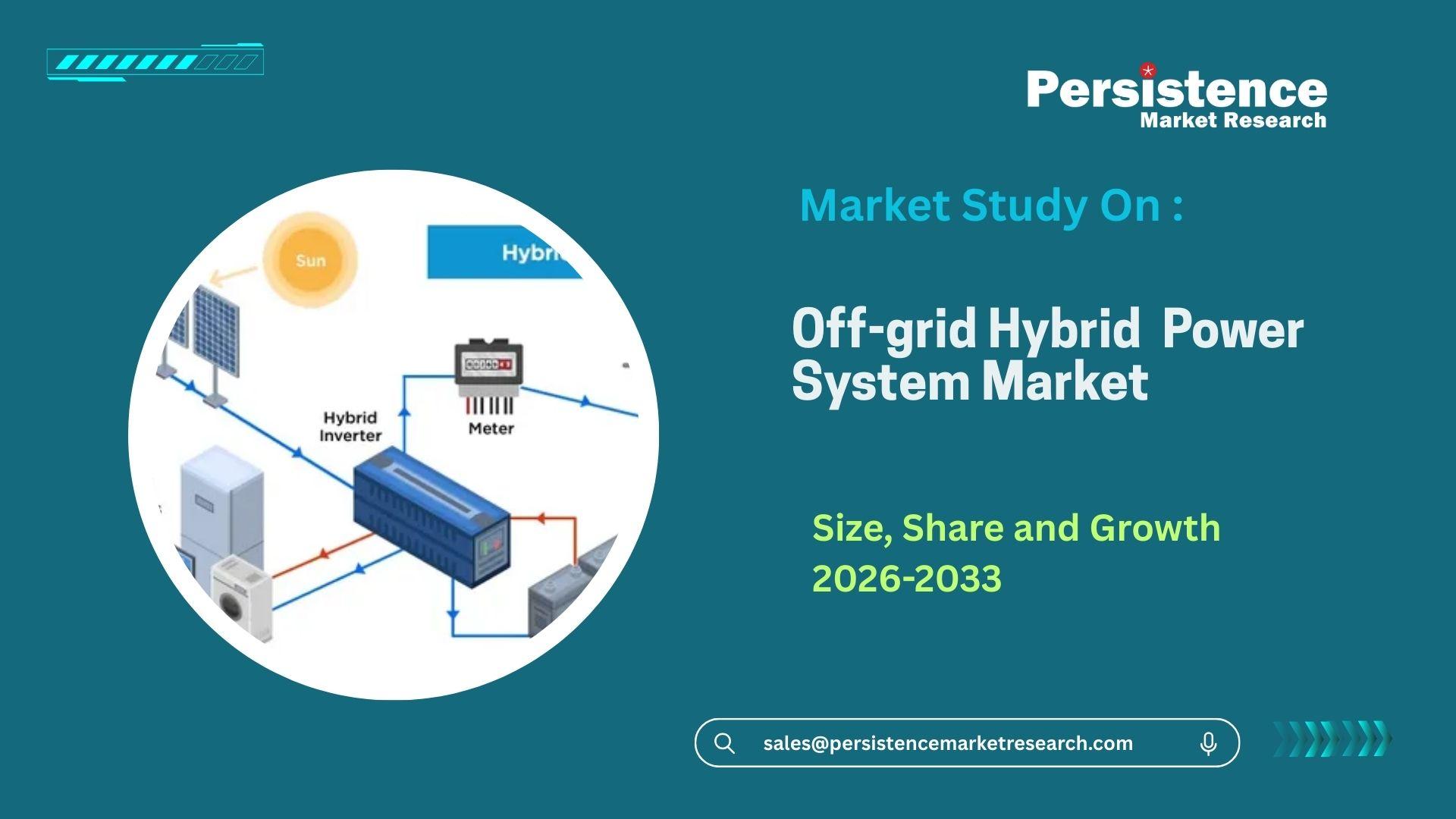
Off-grid hybrid power systems are energy solutions designed to provide electricity to areas that are not connected to the main grid. They integrate multiple power sources, typically combining renewable energy technologies with conventional generation methods such as diesel or natural gas. These hybrid systems are crucial in remote locations where traditional infrastructure is either unavailable or too costly to implement.
The main components of off-grid hybrid systems include:
- Renewable Energy Sources: Solar panels, wind turbines, and micro-hydro generators are the most common renewable energy technologies used. These sources harness nature’s power to generate electricity, which can be stored or used directly.
- Backup Generators: Diesel or gas-powered generators are typically included as a backup when renewable sources are insufficient due to weather conditions or other factors.
- Energy Storage: Batteries or other forms of energy storage are used to store excess power generated during peak production times, ensuring a steady supply of electricity even when renewable sources are not generating power.
- Power Management Systems: These systems control the flow of electricity from various sources, ensuring that the most efficient power is used at any given time and that backup generators are only activated when necessary.
The integration of renewable and conventional energy sources allows for more reliable and sustainable power solutions, especially in areas where the main grid is absent or unreliable.
The Growing Demand for Off-Grid Hybrid Power Systems
The demand for off-grid hybrid power systems has been on the rise for several reasons. Many remote areas, particularly in developing regions, have limited access to electricity from the main grid, creating an urgent need for alternative power solutions. Moreover, the global push for cleaner energy is driving the adoption of renewable technologies, making hybrid systems more cost-effective and appealing.
Several key factors contribute to the growing demand for these systems:
- Decreasing Costs of Renewable Energy: Over the past decade, the cost of renewable energy technologies, especially solar and wind, has dropped significantly. This trend is expected to continue, making renewable energy more affordable for off-grid applications.
- Increasing Rural Electrification Initiatives: Governments and NGOs worldwide are focused on improving energy access in rural areas. Off-grid hybrid systems are a practical solution to this challenge, as they can provide reliable electricity without the need for costly grid infrastructure.
- Advancements in Energy Storage Technologies: One of the main challenges with renewable energy is its intermittent nature. However, significant advancements in energy storage solutions, such as lithium-ion batteries, have improved the efficiency and reliability of hybrid systems.
According to Persistence Market Research, the global off-grid hybrid power system market is expected to be valued at US$3.3 billion in 2026 and is projected to reach US$6.5 billion by 2033, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.3% during the forecast period from 2026 to 2033. This growth is fueled by the decreasing costs of renewable energy, increasing rural electrification initiatives, and advancements in energy storage technologies that improve both system reliability and operational efficiency.
Advantages of Off-Grid Hybrid Power Systems
Off-grid hybrid power systems offer several advantages over traditional power generation methods, particularly in remote and rural areas. These benefits make them an attractive solution for communities that are isolated from the main grid.
- Energy Independence: One of the primary benefits of off-grid hybrid systems is energy independence. By generating and storing their own electricity, off-grid communities can reduce their reliance on imported fuels or unstable grid connections, which may be unreliable or too expensive.
- Sustainability and Environmental Benefits: Hybrid systems that rely on renewable energy sources significantly reduce carbon emissions compared to conventional diesel or gas generators. By using solar, wind, or hydro power, these systems contribute to global efforts to combat climate change.
- Cost Savings: While the initial installation cost of off-grid hybrid systems can be high, over time, they offer significant cost savings. By reducing the need for diesel fuel or expensive grid connections, these systems can help lower energy costs for consumers in remote areas.
- Improved Reliability: Hybrid systems provide more reliable power than single-source systems. By combining renewable energy sources with backup generators, the system can adapt to varying weather conditions and ensure a steady power supply.
- Scalability: Off-grid hybrid systems are highly scalable, meaning they can be tailored to meet the specific needs of a community, whether it's a small village or a larger regional grid. This flexibility allows for cost-effective deployment in various settings.
Key Challenges of Off-Grid Hybrid Power Systems
Despite their many benefits, off-grid hybrid power systems also face several challenges that need to be addressed to maximize their potential. These challenges often relate to technical, financial, and logistical factors.
- High Initial Costs: One of the biggest obstacles to the widespread adoption of off-grid hybrid systems is the high initial cost of installation. While the cost of renewable energy technologies has fallen, hybrid systems still require a significant investment, particularly in energy storage and power management systems.
- Maintenance and Technical Expertise: Maintaining off-grid hybrid systems requires specialized knowledge and skills. In remote areas where technical expertise may be limited, this can pose a significant barrier to effective system operation and maintenance.
- Energy Storage Limitations: Although advancements in energy storage technologies have improved the reliability of hybrid systems, energy storage remains a limitation. Batteries have a finite lifespan and can be costly to replace, which can increase the overall cost of the system.
- Fuel Availability for Backup Generators: In areas where diesel or gas-powered backup generators are used, the availability of fuel can be a concern. Transporting fuel to remote areas can be expensive and logistically challenging, and in some cases, fuel shortages can lead to power disruptions.
- Regulatory and Policy Barriers: In many countries, policies and regulations around renewable energy and off-grid systems are still developing. Lack of clear guidelines or incentives for off-grid hybrid systems can hinder their widespread adoption, especially in developing regions.
The Future of Off-Grid Hybrid Power Systems
Despite these challenges, the future of off-grid hybrid power systems looks promising. As renewable energy technologies continue to evolve and costs decline, these systems are expected to become increasingly affordable and accessible. The integration of smart grids, improved storage technologies, and innovative financing models are all expected to play a significant role in expanding the reach of hybrid power systems.
Several trends are shaping the future of off-grid hybrid systems:
- Increased Integration with Smart Grids: Smart grids, which use advanced communication and automation technologies to optimize energy distribution, are expected to be integrated with off-grid hybrid systems. This integration will allow for more efficient energy management and improve the reliability of power supply.
- Microgrids for Local Energy Solutions: Microgrids are small, localized energy networks that can operate independently or in conjunction with the main grid. The development of microgrids is a key trend, as they offer an efficient way to deliver power to remote communities while allowing for greater control over energy consumption.
- Decentralized Energy Production: The shift toward decentralized energy production is expected to continue, with more communities relying on their own renewable energy sources. This shift will empower local populations and reduce dependence on centralized utilities.
- Innovative Financing Models: To overcome the high initial costs of hybrid systems, new financing models, such as pay-as-you-go (PAYG) schemes, are gaining popularity. These models make it easier for individuals and communities to access off-grid power without significant upfront investment.
Conclusion
Off-grid hybrid power systems offer a promising solution to the energy access challenges faced by remote and underserved communities. By combining renewable energy sources with conventional power generation, these systems provide a sustainable, reliable, and cost-effective alternative to traditional grid-based electricity.
The market for off-grid hybrid systems is expected to continue its rapid growth, driven by advancements in renewable energy, energy storage, and supportive policies. While challenges remain, the future of off-grid hybrid power systems looks bright, with the potential to transform energy access, reduce carbon emissions, and promote energy independence for millions of people worldwide.
As the demand for clean, affordable energy increases, off-grid hybrid systems will play an integral role in ensuring that no community is left behind in the global energy transition.