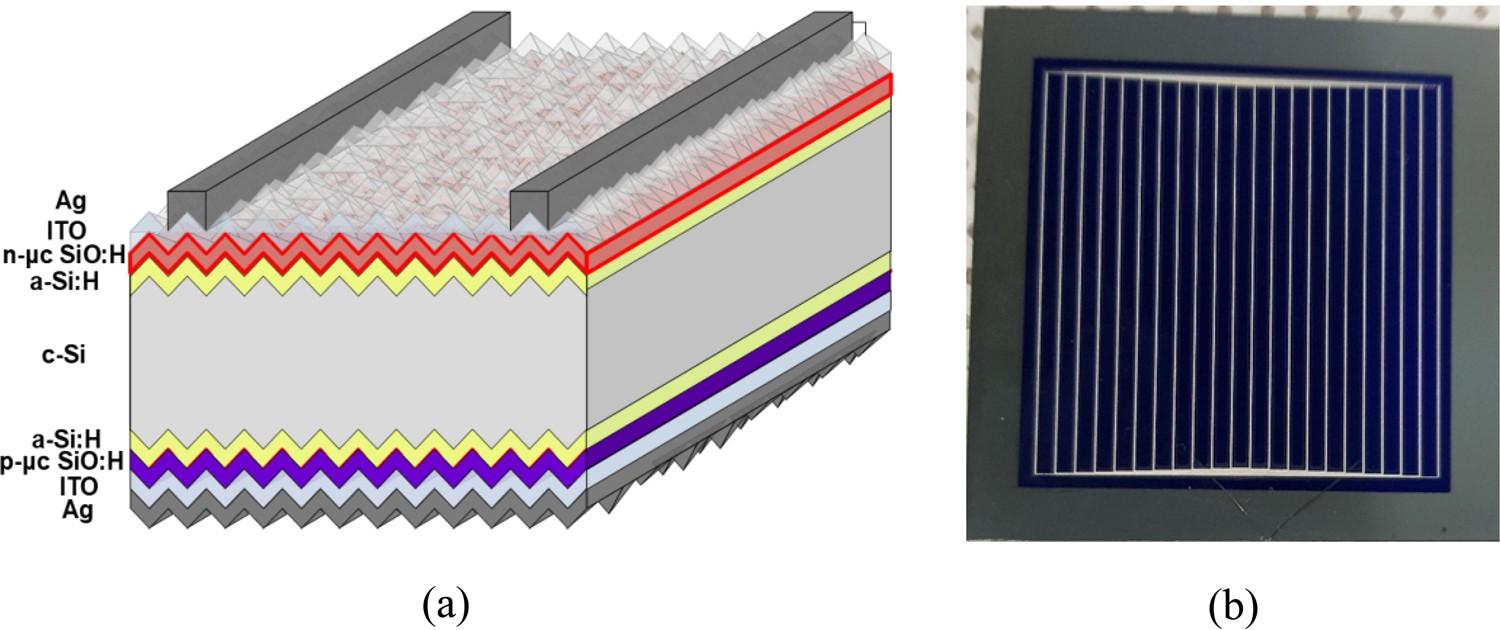
The selective emitter solar cell market represents a significant advancement in photovoltaic technology as the global energy sector accelerates its transition toward renewable and sustainable power sources. Solar energy continues to play a critical role in reducing carbon emissions enhancing energy security and meeting rising electricity demand across residential commercial and industrial sectors. As competition intensifies within the solar industry manufacturers are increasingly focused on improving cell efficiency reducing energy losses and optimizing production processes. Selective emitter solar cells have emerged as an effective solution to address these performance challenges.
Selective emitter solar cells are designed to improve electrical output by reducing recombination losses and enhancing current collection efficiency. By incorporating different doping concentrations across the emitter region these cells allow for lower resistance at the metal contacts while maintaining minimal recombination in non contact areas. This technological innovation leads to higher conversion efficiencies without significantly increasing production complexity. As solar developers and module manufacturers seek cost effective efficiency gains selective emitter technology is becoming a preferred choice in advanced photovoltaic systems.
According to persistence market research The global selective emitter solar cell market size is likely to be valued at US$2.0 billion in 2026 and is expected to reach US$3.9 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 10.5 percent during the forecast period from 2026 to 2033, driven by increasing demand for efficiency gains in solar photovoltaic systems, with selective emitter designs reducing recombination losses and boosting output over standard cells.
Key Market Drivers Accelerating Industry Growth
The growth of the selective emitter solar cell market is driven by several interconnected factors shaping the global solar energy landscape. One of the most important drivers is the rising demand for high efficiency solar modules. As land availability becomes limited and installation costs increase developers prioritize technologies that deliver higher power output per unit area. Selective emitter cells offer measurable efficiency improvements that directly enhance project economics.
Government policies and renewable energy mandates are another major growth driver. Many countries have introduced aggressive solar deployment targets supported by subsidies tax incentives and feed in tariffs. These policies encourage the adoption of advanced cell technologies that improve energy yield and system performance.
Cost reduction across the solar value chain is also fueling market expansion. Selective emitter technology enables manufacturers to achieve efficiency gains without substantially increasing material usage or production expenses. This aligns with industry efforts to reduce the levelized cost of electricity from solar power.
Technological advancements in laser processing and precision doping further support market growth. Improved manufacturing techniques have increased yield rates reduced defect levels and enhanced scalability making selective emitter solar cells more commercially attractive.
Market Segmentation by Technology Type
The selective emitter solar cell market can be segmented based on the technology used to create selective doping patterns. Laser doped selective emitter technology is one of the most widely adopted approaches. It uses laser beams to locally increase doping concentration under metal contacts providing precise control and high repeatability. This method is favored for its compatibility with mass production.
Etched back selective emitter technology represents another important segment. This approach involves selectively removing heavily doped regions after initial diffusion to create optimized emitter profiles. Although slightly more complex this method offers excellent performance improvements and uniformity.
Ion implantation based selective emitter technology is gaining attention for its high precision and consistency. This method allows accurate control over doping depth and concentration resulting in superior electrical characteristics. As implantation equipment becomes more cost effective adoption of this technology is expected to increase.
Each technology segment offers distinct advantages depending on production scale efficiency targets and capital investment considerations.
Application Areas and End Use Sectors
Selective emitter solar cells are widely used across residential commercial utility scale and industrial solar installations. Residential rooftop systems benefit from higher efficiency cells that maximize energy output in limited space. Improved performance enhances return on investment for homeowners and increases system attractiveness.
Commercial solar installations such as office buildings warehouses and shopping complexes also benefit from selective emitter technology. Higher efficiency modules reduce installation footprint and support corporate sustainability goals while lowering energy costs.
Utility scale solar power plants represent a major application segment. Large scale developers prioritize technologies that deliver incremental efficiency gains at scale. Even small improvements in cell efficiency translate into significant increases in total power generation and revenue over the project lifetime.
Industrial applications including off grid power systems and specialized energy solutions further expand the market scope. As industries seek reliable renewable power selective emitter solar cells provide a performance advantage that supports operational stability.
Regional Market Trends and Growth Opportunities
The selective emitter solar cell market demonstrates strong regional growth patterns influenced by solar adoption rates manufacturing capacity and policy frameworks.
· Asia Pacific is the leading region driven by large scale solar deployment and strong manufacturing ecosystems in countries such as China India South Korea and Japan. The region benefits from high investment in photovoltaic research and production infrastructure.
· China remains a dominant market due to its position as the world largest solar module producer. Continuous improvements in cell efficiency are critical for maintaining competitiveness which supports widespread adoption of selective emitter technology.
· North America represents a rapidly growing market supported by favorable renewable energy policies corporate sustainability initiatives and rising residential solar installations. The United States in particular is investing in advanced solar technologies to enhance grid resilience and energy independence.
· Europe continues to show steady growth driven by climate targets energy transition goals and supportive regulatory frameworks. Countries such as Germany Spain and France are adopting high efficiency solar technologies to maximize output from limited land resources.
· Latin America the Middle East and Africa are also creating new opportunities as solar power becomes a preferred solution for energy access and diversification.
Competitive Landscape and Industry Participants
The selective emitter solar cell market is highly competitive with the presence of global photovoltaic manufacturers technology providers and equipment suppliers
- Tata Power Solar Systems
- Trina Solar
- SolarWorld
- Suniva
- JinkoSolar
- Pionis Energy
Innovation and intellectual property play a critical role in shaping competitive dynamics. Companies with proprietary selective emitter processes and advanced cell architectures gain a technological edge in performance and cost efficiency.
Future Outlook and Emerging Trends
The future of the selective emitter solar cell market appears highly promising as global demand for high efficiency photovoltaic solutions continues to rise. Ongoing innovation in laser processing automation and digital manufacturing will further improve production efficiency and reduce costs.
Integration of selective emitter technology with advanced cell architectures is expected to enhance performance even further. Hybrid designs combining selective emitter features with passivation and advanced contacts will unlock new efficiency benchmarks.
Sustainability considerations will play an increasingly important role. Manufacturers are focusing on reducing energy consumption waste generation and carbon footprint during cell production. Selective emitter processes that align with green manufacturing principles will gain preference.
As solar energy becomes a cornerstone of global energy systems selective emitter solar cells will remain a critical technology enabling higher output improved reliability and better economic returns.
Conclusion
The global selective emitter solar cell market is positioned for robust growth driven by rising demand for efficiency improvements cost effective renewable energy solutions and supportive policy frameworks. By reducing recombination losses and enhancing electrical performance selective emitter technology delivers meaningful gains over conventional solar cells.
Expanding applications across residential commercial and utility scale installations combined with strong regional growth dynamics underscore the market potential. Although challenges related to manufacturing complexity and competition from alternative technologies persist continuous innovation and investment are addressing these barriers.
As the solar industry evolves toward higher performance and sustainability selective emitter solar cells will play a vital role in shaping the future of photovoltaic power generation worldwide.