A modern, enterprise-class risk management platform is a sophisticated and highly integrated system, not a simple standalone application. A complete Risk Management Software Market Solution can be understood as a multi-layered architecture designed to support the entire risk lifecycle, from identification to mitigation and reporting. This end-to-end solution provides a centralized "system of record" for all risk-related information and acts as a "system of engagement" to coordinate risk management activities across the entire organization. Understanding the key components of this architecture—the foundational data layer, the core application modules, and the user-facing analytics and reporting layer—is essential to appreciating how these platforms transform the abstract concept of risk into a manageable and actionable business discipline.
At the base of the solution is the foundational data and integration layer. This is the component responsible for creating a single, unified view of the organization's assets, processes, and controls. This often involves a central repository, or Configuration Management Database (CMDB), that maps out the relationships between business processes, the IT systems that support them, and the regulations they are subject to. A crucial part of this layer is its ability to integrate with and pull data from a wide variety of other enterprise systems via APIs. This includes connecting to HR systems for employee data, ERP systems for financial data, and IT security tools for vulnerability data. This ability to aggregate and normalize data from across the enterprise is what enables a truly holistic and contextual view of risk.
The heart of the solution is the suite of core application modules. These are the functional components that operationalize the risk management process. This typically includes a Risk and Control Self-Assessment (RCSA) module, where business users can identify and assess the risks in their own areas. It includes an Issue and Action Management module to track the remediation of identified weaknesses or control failures. There is often a dedicated Audit Management module for internal audit teams and a Compliance Management module to map controls to specific regulations and automate evidence collection. For more mature solutions, there will be specialized modules for areas like Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM), Business Continuity Management (BCM), and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) risk management, each with its own tailored workflows and content.
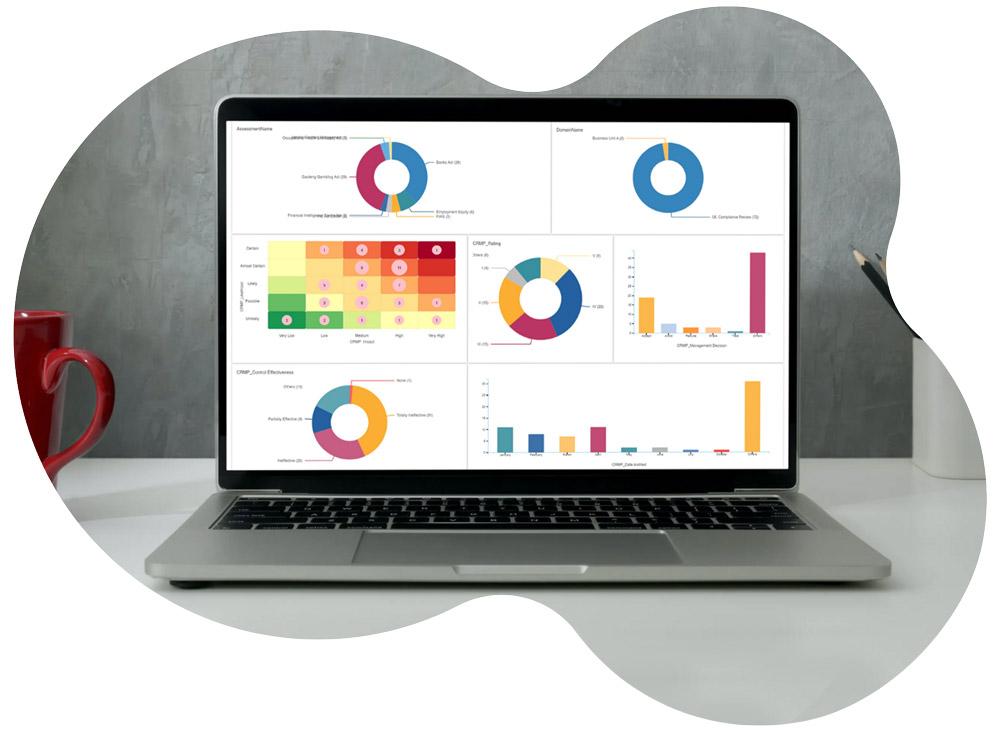
Finally, the value of the entire solution is delivered to its various users through the analytics, reporting, and user experience layer. This is the component that transforms the vast amounts of data in the system into actionable intelligence. For risk managers and business users, it provides personalized dashboards and task lists that show them exactly what they need to do. For senior leadership and the board of directors, it provides high-level, interactive dashboards and reports, such as risk heat maps and trend analyses, that give them an at-a-glance view of the organization's risk posture. A modern solution has a highly configurable reporting engine that can generate the specific reports needed for regulators, auditors, and other stakeholders. This user-friendly and powerful reporting capability is what makes the software a true tool for strategic governance.
Top Trending Reports: