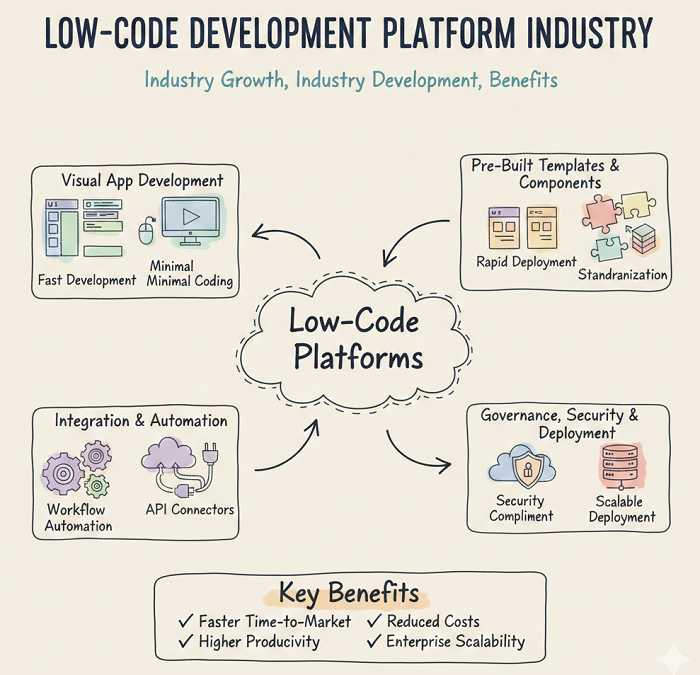
The Low Code Development Platform Market Value proposition is rooted in time savings, reduced engineering effort, and faster iteration cycles. Organizations often see value when low code reduces application backlog and enables process automation that eliminates manual steps. By providing visual development, reusable components, and prebuilt connectors, platforms can cut delivery timelines for common workflow apps from months to weeks. This speed supports business agility, allowing teams to respond to policy changes, customer demands, and operational disruptions quickly. Value also appears in standardization: shared components and templates reduce rework and improve consistency across departments. For IT leaders, low code can improve utilization of scarce developer talent by reserving custom engineering for high-complexity problems. For business teams, structured citizen development can produce useful internal tools under governance. Many organizations also count value from improved user experience and reduced error rates in manual processes. Over time, low code value is measured by throughput, reliability, and the ability to scale solutions enterprise-wide.
Financial evaluation extends beyond licensing to include implementation and operational costs. Organizations compare platform pricing models—per user, per app, per environment, or consumption-based—against expected adoption scale. Hidden costs can arise from integration work, data migration, and building governance structures. Conversely, strong vendor enablement and integrator support can accelerate ROI by reducing trial-and-error. Value improves when platforms offer robust security, auditability, and compliance support, since these reduce risk and speed approvals for production deployment. Platform reliability and uptime are also value multipliers; when low code apps run critical workflows, outages can be expensive. Another dimension is maintainability: applications built with standardized components and clear lifecycle tooling can be updated faster over time than custom-built systems. Organizations also benefit when platforms support multi-channel delivery—web, mobile, and portals—without separate codebases. The best value outcomes occur when low code is adopted as a strategic platform with clear use-case prioritization rather than scattered experimentation. In that model, benefits compound as reusable assets grow.
Operational value increases when low code connects directly to core systems and automates end-to-end workflows. For example, onboarding workflows can trigger identity provisioning, training assignments, equipment requests, and compliance checks automatically. Customer service apps can unify case intake, routing, and escalation with integrated notifications and dashboards. Field operations can benefit from mobile forms, offline capture, and automated synchronization, reducing paperwork and delays. In finance and procurement, low code can streamline approvals, audit trails, and exception handling, improving compliance and cycle time. Many platforms also support analytics and reporting, enabling leaders to measure bottlenecks and refine processes continuously. When low code is paired with RPA or process mining, organizations can identify automation opportunities and implement improvements rapidly. This creates a feedback loop where data reveals inefficiency, low code delivers fixes, and metrics validate results. Such loops strengthen the long-term value case by making continuous improvement easier. The practical outcome is lower operational friction and faster decision-making.
Value can be reduced by poor governance, duplication, and weak architectural discipline. Without standards, organizations may create many small apps that are hard to maintain, raising long-term costs. To protect value, mature adopters use a center of excellence, enforce design patterns, and require security reviews before deployment. Vendor lock-in concerns also influence value perception, so buyers prefer platforms with extensibility and integration options that preserve flexibility. Looking forward, market value is likely to increase as AI-assisted development improves productivity and as platforms strengthen DevOps and observability features. Organizations will keep prioritizing speed-to-solution, but they will demand enterprise reliability as low code apps become mission-critical. The platforms delivering measurable cycle-time reductions, strong governance, and scalable integration will offer the strongest value. In many enterprises, low code is shifting from “faster apps” to “faster operations,” expanding the value narrative across the entire business.
Top Trending Reports:
Point To Point Microwave Antenna Market